Breaking Down the Latest Economic News in the United States
The 2026 Economic Landscape: A Pivotal Moment for the United States
As 2026 unfolds, the United States finds itself at a critical juncture where economic resilience, structural transformation and policy experimentation intersect in ways that will shape growth, employment and competitiveness for the rest of the decade. For the readership of USA-Update.com, which closely follows developments in the economy, finance, jobs, regulation, energy and consumer trends, the current environment presents both opportunities and uncertainties that demand careful analysis rather than quick conclusions. The latest economic news is not defined by a single headline or indicator but by a complex interplay of moderating inflation, evolving labor markets, shifting global trade patterns, accelerating technological change and a recalibration of monetary and fiscal policy.
The American economy has moved beyond the immediate post-pandemic recovery phase and is now navigating a period that economists increasingly describe as normalization with structural change. Growth has slowed from earlier peaks but has remained positive, consumer spending is more selective yet still robust in key categories, and business investment is being reoriented toward digital infrastructure, clean energy and advanced manufacturing. Readers seeking a concise overview of the broader economic context can explore the evolving themes covered on the USA-Update.com economy page, where macroeconomic developments are tracked against global and domestic trends.
In this environment, understanding the latest economic news in the United States means going beyond headline GDP numbers and unemployment rates to examine how policy choices, corporate strategies, technological innovation and consumer behavior are reshaping the foundations of growth. It also requires a clear sense of how developments in North America, Europe, Asia and other regions feed back into the U.S. outlook, as well as how American decisions influence global markets and supply chains.
Growth, GDP and the Shift from Recovery to Realignment
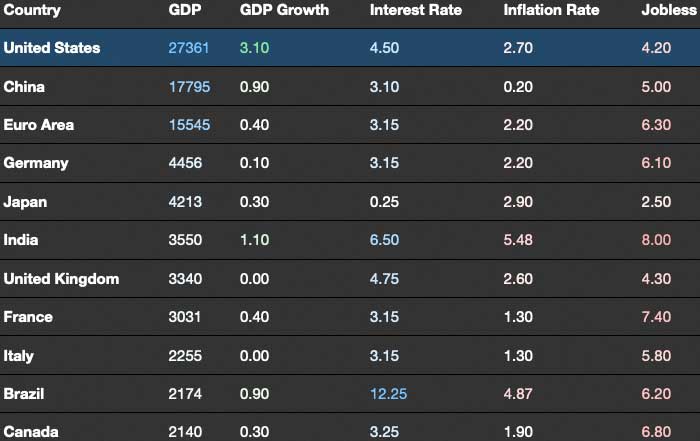
Recent data from institutions such as the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis show that real GDP growth in the United States has settled into a more moderate range compared to the rapid rebound that followed the height of the COVID-19 crisis. While quarterly growth rates fluctuate, underlying trends point to an economy that is expanding at a sustainable but unspectacular pace, constrained by demographic factors, productivity challenges and tighter financial conditions but supported by strong corporate balance sheets, a resilient services sector and ongoing investment in technology and infrastructure. Readers can monitor updated GDP and national accounts information through the BEA's official releases and complement that perspective with broader analysis from organizations like the OECD, which regularly reviews member country performance and structural policies.
This period of realignment is characterized by a rebalancing of growth drivers. The earlier phase of stimulus-driven consumption and extraordinary fiscal support has given way to more targeted public spending, notably in infrastructure, semiconductor manufacturing and clean energy, inspired by legislation such as the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act and the CHIPS and Science Act. These initiatives, tracked closely by outlets like USA-Update.com on its business and technology sections, are gradually shifting the composition of GDP toward investment in productive capacity and away from purely consumption-led expansion.
At the same time, global developments continue to influence U.S. growth. Slower expansion in Europe and parts of Asia, persistent geopolitical tensions and realignments in global supply chains all affect export demand, capital flows and investor sentiment. Institutions such as the International Monetary Fund provide regular updates on the global outlook that help contextualize U.S. performance within broader international trends, while World Bank research highlights longer-term structural challenges related to productivity, inequality and climate resilience.
Inflation, Interest Rates and the New Monetary Policy Balancing Act
One of the most closely watched aspects of the latest economic news in the United States remains the trajectory of inflation and the response of the Federal Reserve. After the surge in price pressures that followed the pandemic and supply chain disruptions, inflation has moderated but remains a central concern for policymakers, businesses and households. Headline inflation has moved closer to the Federal Reserve's longer-run target, yet underlying measures such as core inflation and services inflation continue to be scrutinized for signs of persistence or renewed acceleration.
The Federal Reserve, through its Federal Open Market Committee, has shifted from an aggressive rate-hiking cycle to a more cautious, data-dependent stance, balancing the risks of doing too much and constraining growth against the risks of doing too little and allowing inflation expectations to become unanchored. Market participants closely analyze each policy statement, economic projection and press conference, drawing on real-time data from sources like the Federal Reserve Economic Data (FRED) maintained by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis. Financial professionals and informed readers can also follow commentary from institutions such as the Bank for International Settlements, which examines how global financial conditions and cross-border capital flows interact with national monetary policies.
For the audience of USA-Update.com, this monetary policy environment has direct implications for borrowing costs, mortgage rates, corporate investment decisions and valuation levels across equities, bonds and alternative assets. The site's finance section regularly addresses how interest rate expectations influence both institutional and retail investment strategies, as well as how banks, insurers and asset managers adjust their business models in response to changing yield curves and regulatory expectations.
Labor Markets, Jobs and the Changing Nature of Work
Despite tighter financial conditions, the U.S. labor market has remained surprisingly resilient, with unemployment rates near historically low levels and job openings still elevated in several sectors, even as hiring has cooled from its earlier pace. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics continues to report solid employment gains in areas such as health care, professional services, technology-adjacent roles, logistics and advanced manufacturing, while some consumer-facing sectors experience more volatility. Wage growth has moderated from previous peaks but remains above pre-pandemic averages in many occupations, particularly those requiring specialized skills or offering flexible work arrangements.
The latest employment news is not only about headline job numbers but also about the evolving nature of work, the rise of hybrid and remote models, and the reconfiguration of skills demanded by employers. Organizations like the World Economic Forum have documented how digitalization, automation and artificial intelligence are reshaping job profiles, with new roles emerging in data analysis, cybersecurity, green technologies and human-machine collaboration. For workers, this shift underscores the importance of continuous learning and upskilling, while for employers, it highlights the need to invest in training, inclusive hiring practices and adaptable organizational structures.
Readers of USA-Update.com can follow developments in hiring trends, wage dynamics and workplace transformations through both the jobs and employment pages, which increasingly focus on how companies across the United States and North America are redesigning their talent strategies to compete in a global market. From the perspective of economic policy, initiatives aimed at workforce development, apprenticeships and community college partnerships are becoming central components of strategies to enhance productivity and ensure that growth is broadly shared across regions and demographic groups.
🇺🇸 2026 U.S. Economic Landscape
Moderate Sustainable Expansion
Economy transitions from recovery to realignment with sustainable growth, supported by infrastructure investment and digital transformation initiatives.
Monetary Policy Balance
Federal Reserve adopts data-dependent stance as inflation moderates toward target, balancing growth constraints with price stability goals.
Resilient Employment
Near-historic low unemployment with evolving work models. Healthcare, tech, and advanced manufacturing lead hiring while skills transformation accelerates.
Automation Wave
Major firms drive AI deployment across sectors, promising productivity gains but requiring workforce training and ethical governance frameworks.
Clean Energy Investment
Accelerating shift toward renewables, EVs, and grid modernization balances security, affordability, and decarbonization amid complex regional dynamics.
Selective Spending Patterns
Value-conscious consumers prioritize experiences and digital services while e-commerce and omnichannel retail reshape the marketplace.
Enhanced Oversight
Government agencies assertively address tech platforms, financial institutions, and supply chains balancing innovation with consumer protection.
Strategic Realignment
Emphasis on resilient supply chains and diversification drives nearshoring partnerships while navigating complex geopolitical relationships.
Technology, Innovation and Productivity: The AI and Automation Wave
No discussion of the latest U.S. economic news in 2026 is complete without a detailed look at the rapid acceleration of technological innovation, particularly in artificial intelligence, automation, cloud computing and digital infrastructure. Major American firms such as Microsoft, Alphabet, Amazon, NVIDIA and Meta Platforms continue to lead global investment in AI research and deployment, while a growing ecosystem of startups and mid-sized companies is bringing AI-enabled tools to sectors ranging from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare, finance and entertainment. Analysts tracking these developments often turn to resources such as MIT Technology Review or the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence to understand the broader implications for productivity, employment and regulation.
The potential for AI and automation to boost productivity is significant, particularly in an economy facing demographic headwinds and skills mismatches. Automation of routine tasks can free human workers to focus on higher-value activities, while advanced analytics can enhance decision-making in areas such as supply chain management, energy optimization and personalized medicine. However, realizing these productivity gains requires complementary investments in worker training, organizational change and data governance. Policymakers and business leaders are increasingly aware that technology adoption without adequate attention to human capital and ethical frameworks can exacerbate inequality and erode trust.
For the audience of USA-Update.com, which closely follows both technology and business trends, the key question is not whether AI will transform the economy but how quickly and in what ways, and which sectors and regions will benefit most. The United States remains at the forefront of global innovation, yet competition from Europe, China, South Korea, Japan and other technology-intensive economies is intensifying, prompting renewed focus on research funding, intellectual property protection and cross-border collaboration. Institutions like the U.S. National Science Foundation and the OECD provide valuable insight into innovation ecosystems and R&D trends across leading economies.
Energy, Climate Policy and the Economics of the Transition
Energy markets and climate policy have become central to the U.S. economic conversation, with 2026 marking a phase in which ambition, regulation and private investment are beginning to converge in more tangible ways. The United States is working to balance energy security, affordability and decarbonization, a challenge made more complex by global geopolitical tensions, evolving technologies and regional differences in resource endowments and regulatory frameworks. The U.S. Energy Information Administration offers detailed data and projections on energy production, consumption and prices, while international organizations such as the International Energy Agency provide comparative analysis across major economies.
In recent years, federal and state policies have accelerated investment in renewable energy, grid modernization, electric vehicles and energy efficiency, supported by tax incentives, public-private partnerships and long-term emissions targets. Major companies like Tesla, General Motors, Ford, NextEra Energy and Duke Energy are reshaping their strategies to align with a lower-carbon future, while traditional oil and gas firms, including ExxonMobil and Chevron, are investing in carbon capture, hydrogen and other transitional technologies. The economics of this transition are complex, involving upfront capital expenditures, evolving regulatory requirements and the need to manage impacts on workers and communities dependent on legacy energy industries.
Readers of USA-Update.com can follow these developments through the dedicated energy section, which increasingly highlights the intersection between energy policy, technological innovation, employment and regional economic development. The transition also has direct implications for consumers, affecting gasoline and electricity prices, home heating costs and the affordability of electric vehicles and energy-efficient appliances. Organizations such as the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and the U.N. Environment Programme provide additional context on how U.S. policies fit into broader global climate commitments and environmental standards.
Consumer Behavior, Confidence and the New Spending Patterns
Consumer spending remains the backbone of the U.S. economy, and the latest economic news reveals a nuanced picture where overall consumption is holding up but spending patterns are changing in response to inflation, interest rates, digitalization and shifting preferences. Surveys from institutions such as The Conference Board and the University of Michigan show that consumer confidence has improved from previous lows but remains sensitive to news about inflation, job security, geopolitical risks and financial market volatility. Households are increasingly value-conscious, trading down in some categories while still prioritizing experiences, travel, health and digital services.
The rise of e-commerce and digital payment platforms continues to reshape the retail landscape, benefiting major players like Amazon, Walmart and Target, while also creating opportunities for niche online brands and direct-to-consumer models. At the same time, brick-and-mortar retail is evolving toward more experiential formats, leveraging data analytics, loyalty programs and omnichannel strategies to maintain relevance. Regulatory bodies such as the U.S. Federal Trade Commission are paying closer attention to issues related to digital advertising, data privacy and competition, which have implications for both consumers and businesses operating in increasingly concentrated markets.
For USA-Update.com readers interested in how these trends affect daily life and purchasing decisions, the consumer section and lifestyle section provide ongoing coverage of price trends, product innovation, digital services and shifts in entertainment and travel spending. The interplay between consumer sentiment, credit conditions and labor income will remain a key determinant of the U.S. growth path over the next several years, especially as households adjust to a world of higher baseline interest rates and more volatile energy and housing costs.
Financial Markets, Corporate Strategy and Capital Allocation
Financial markets in 2026 reflect a delicate balance between optimism about technological innovation and productivity gains on the one hand and concerns about valuations, debt levels and geopolitical risks on the other. U.S. equity indices have experienced periods of volatility as investors reassess earnings prospects, discount rates and sectoral leadership. Technology, healthcare and industrials tied to infrastructure and clean energy continue to attract significant capital, while more interest-rate-sensitive sectors such as real estate and certain segments of consumer discretionary face greater scrutiny. Market participants rely on data and analysis from organizations like S&P Global, Bloomberg and Morningstar to navigate this complex environment.
Corporate strategy has adapted to this new reality, with many companies emphasizing capital discipline, resilient supply chains, digital transformation and environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations. Large multinationals headquartered in the United States, including Apple, Johnson & Johnson, Coca-Cola, PepsiCo and Procter & Gamble, are rebalancing their geographic exposure and product portfolios to reflect changing demand patterns in North America, Europe, Asia and emerging markets. At the same time, the private equity and venture capital sectors remain active, though more selective, focusing on high-conviction themes such as AI, cybersecurity, climate technology and healthcare innovation.
The USA-Update.com finance page pays close attention to how these shifts in capital allocation influence broader economic outcomes, from job creation and wage growth to regional development and innovation ecosystems. Regulatory developments, including capital requirements for banks, disclosure rules for public companies and oversight of digital assets, are also shaping the financial landscape. Agencies such as the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission and the Financial Stability Board play critical roles in monitoring systemic risks and setting standards that affect both U.S. and global markets.
Regulation, Policy and the Evolving Role of Government
Regulation and public policy have become central themes in the latest U.S. economic news, reflecting heightened scrutiny of large technology platforms, financial institutions, healthcare systems, energy producers and cross-border supply chains. The United States is engaged in a broader debate about how to balance innovation and competition with consumer protection, data privacy, cybersecurity and national security concerns. Legislative and regulatory initiatives in areas such as antitrust enforcement, digital platform oversight, climate disclosure, labor standards and trade policy are reshaping the operating environment for businesses of all sizes.
Agencies including the U.S. Department of Justice, the Federal Trade Commission, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau and the Department of Labor are taking more assertive stances in several domains, while Congress and the executive branch continue to explore new frameworks for issues such as artificial intelligence governance, cryptocurrency regulation and cross-border data flows. Internationally, coordination with partners in the European Union, the United Kingdom, Canada, Japan, South Korea and other jurisdictions is increasingly important to avoid regulatory fragmentation and to address issues that transcend national borders, such as cyber threats, climate change and global financial stability.
Readers of USA-Update.com can track these developments through the regulation section, which places particular emphasis on how policy changes affect businesses, investors and workers in the United States and across North America. For companies operating globally, staying informed about evolving standards and compliance requirements is not merely a legal obligation but a strategic necessity that can influence market access, brand reputation and long-term competitiveness.
International Trade, Geopolitics and the U.S. Global Position
The international dimension of the U.S. economy has become more complex and politically charged, with trade policy, supply chain strategies and geopolitical alliances playing increasingly prominent roles in economic decision-making. The United States remains deeply integrated into global trade networks, with significant flows of goods, services and capital connecting it to Europe, Asia, South America, Africa and other regions. However, the experience of recent years has led policymakers and corporate leaders to place greater emphasis on resilience, diversification and national security considerations, particularly in sectors such as semiconductors, pharmaceuticals, critical minerals and advanced manufacturing.
Relations with major trading partners and competitors, including the European Union, China, Canada, Mexico, Japan, South Korea and the United Kingdom, continue to evolve, with ongoing negotiations, disputes and collaborations shaping the rules of the game. Institutions such as the World Trade Organization and regional trade agreements provide frameworks for resolving conflicts and promoting openness, yet unilateral measures and bilateral arrangements have become more common tools in the pursuit of strategic objectives. For example, export controls on advanced technologies, investment screening mechanisms and targeted tariffs have become instruments of economic statecraft.
The USA-Update.com international page examines how these developments affect U.S. businesses, workers and consumers, highlighting both the risks of fragmentation and the opportunities arising from nearshoring, friend-shoring and new trade corridors. Countries such as Mexico, Canada, Brazil, India, Vietnam and several Southeast Asian economies are increasingly seen as key partners in diversified supply chains, while Europe remains a critical market for U.S. exports and a collaborator on regulatory standards, climate policy and digital governance.
Travel, Tourism and the Services Economy
The services sector, particularly travel and tourism, has long been a major contributor to U.S. GDP, employment and export earnings, and its recovery and transformation since the pandemic are important components of the current economic narrative. By 2026, international travel to and from the United States has largely rebounded, supported by improved health conditions, digital travel tools, flexible work arrangements and pent-up demand for leisure and business trips. Major U.S. airlines such as Delta Air Lines, American Airlines and United Airlines, along with global hotel groups like Marriott International and Hilton, have adapted by investing in technology, loyalty programs and new routes that connect key hubs in North America, Europe, Asia and beyond.
Organizations such as the U.S. Travel Association and the World Travel & Tourism Council provide data and analysis on visitor flows, spending patterns and policy issues such as visa processing, airport infrastructure and sustainability standards. The integration of digital health credentials, biometric identification and contactless services has improved efficiency but also raised questions about privacy, data security and inclusivity. For many U.S. cities and states, tourism remains a vital source of revenue and employment, supporting local businesses in hospitality, entertainment, retail and transportation.
For readers of USA-Update.com, the travel section offers insights into how these trends intersect with broader economic conditions, such as exchange rates, energy prices and consumer confidence. The services sector more broadly, including education, healthcare, financial services and creative industries, continues to be a key driver of U.S. economic strength and a source of export revenue, particularly in knowledge-intensive and high-value-added segments.
Entertainment, Media and the Digital Consumer Economy
The entertainment and media industries provide another lens through which to view the latest U.S. economic news, as they reflect both changing consumer preferences and the broader impact of digital technologies on business models and labor markets. The United States remains home to globally influential entertainment companies such as Disney, Netflix, Warner Bros. Discovery, Paramount Global and Comcast, as well as leading music, gaming and sports organizations. These firms are navigating a landscape in which streaming, social media, gaming and user-generated content compete for attention and subscription dollars, while traditional television and print media continue to face structural challenges.
Digital platforms like YouTube, TikTok and Spotify have transformed how content is created, distributed and monetized, raising questions about revenue sharing, intellectual property rights and the working conditions of creators and gig-economy participants. Regulatory bodies in the United States and abroad are increasingly focused on issues such as content moderation, algorithmic transparency, competition and the mental health impacts of digital media consumption. Industry research from organizations like PwC and Deloitte helps illuminate long-term trends in advertising, subscription models and consumer behavior across demographics and regions.
The USA-Update.com entertainment section provides coverage of these developments with a focus on their economic implications, including investment flows into content production, employment in creative industries and the role of entertainment in shaping cultural exports and soft power. For businesses outside the media sector, the evolution of entertainment and digital engagement offers lessons in customer experience, data analytics and brand building in a fragmented attention economy.
Regional Perspectives: North America, Europe, Asia and Beyond
While the United States remains the primary focus for USA-Update.com, the economic news of 2026 cannot be fully understood without considering regional developments across North America, Europe, Asia, South America, Africa and Oceania. Canada and Mexico, as key partners in the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), play crucial roles in integrated supply chains for automotive, aerospace, agriculture, energy and manufacturing. Economic performance in these countries influences and is influenced by U.S. trade, investment and labor market dynamics, creating a highly interconnected North American economy.
In Europe, countries such as Germany, France, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark and Finland are grappling with their own challenges related to energy security, demographic change, digital transformation and fiscal policy, all of which have implications for transatlantic trade and investment. The European Central Bank and national governments continue to adjust monetary and fiscal policies in response to inflation and growth concerns, while the European Union advances initiatives in digital regulation, green transition and industrial policy that affect U.S. companies operating in the region.
Across Asia, major economies including China, Japan, South Korea, India, Singapore, Thailand and Malaysia are at different stages of economic transition, with varying growth rates, policy priorities and geopolitical alignments. China's economic trajectory, in particular, remains a central factor in global demand for commodities, intermediate goods and advanced technology, as well as in the strategic calculations of U.S. policymakers and corporations. Institutions such as the Asian Development Bank and the Bank of Japan provide valuable insight into regional trends that feed back into the U.S. outlook.
In South America and Africa, countries like Brazil, South Africa and others are pursuing strategies to leverage natural resources, young populations and digitalization to boost growth, even as they face challenges related to governance, infrastructure and climate vulnerability. For U.S. businesses and investors, these regions represent both opportunities and risks, requiring careful assessment of political stability, regulatory frameworks and local partnerships.
What the Latest Economic News Means for USA-Update.com Readers
For the business-focused audience of USA-Update.com, the latest economic news in the United States in 2026 underscores the importance of informed, nuanced and forward-looking analysis. The economy is neither in crisis nor in a simple boom; rather, it is in a complex transition characterized by moderate growth, evolving inflation dynamics, tight but shifting labor markets, rapid technological change, ambitious energy and climate policies, and a more fragmented and competitive global landscape. Success for businesses, investors, workers and policymakers will depend on the ability to adapt to these changes, manage risks and seize emerging opportunities.
The site's coverage across the news, economy, business, technology, finance, jobs, international, travel, energy, consumer and other sections is designed to provide an integrated view of these developments, grounded in experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness. By drawing on high-quality data, expert commentary and real-world case studies, USA-Update.com aims to equip its readers with the insights they need to make informed decisions in an environment where economic headlines are abundant but clear guidance is scarce.
As 2026 progresses, the central themes to watch include the durability of disinflation, the pace and inclusiveness of productivity gains driven by AI and automation, the effectiveness of energy transition policies, the evolution of regulatory frameworks for technology and finance, and the resilience of global trade and investment flows in the face of geopolitical tensions. For those who follow these issues closely through USA-Update.com and other trusted sources, the latest economic news is not merely a series of isolated events but part of a broader narrative about how the United States, North America and the wider world are redefining growth, prosperity and competitiveness in a new era.