America's New Department of War: What the 2025 Rebrand Means for Power, Prosperity, and the Public
A Historic Rebrand in an Uncertain World
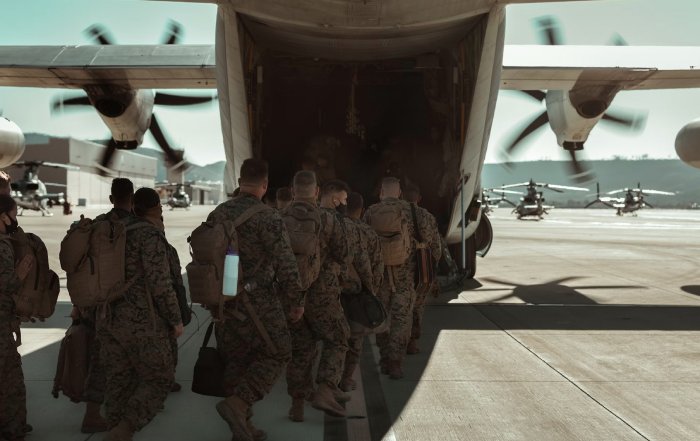
In early 2025, the United States government confirmed one of the most controversial strategic branding decisions in modern American history: the Pentagon's Department of Defense would be officially renamed the Department of War. By 2026, the new name is fully in use across official documents, congressional hearings, and international diplomacy, and its implications are still unfolding. For readers of usa-update.com, which closely follows developments in the U.S. and across North America and key global regions, this shift is more than a semantic change; it is a lens through which to understand evolving U.S. power, domestic priorities, and the future of the international order.
The rebrand arrived at a moment of intensifying geopolitical competition, especially with China, rising populism and polarization within the United States, and a world economy still adjusting to supply chain shocks, energy transitions, and technological disruption. Just weeks before the announcement, China staged a meticulously choreographed military parade in Beijing, a display of precision and symbolism that projected confidence, discipline, and a narrative of "peaceful development" to a global audience. Against that backdrop, Washington's decision to adopt the language of "war" rather than "defense" signaled a radically different strategic posture, and one that many allies, adversaries, and neutral observers have interpreted as a public embrace of permanent conflict readiness.
For business leaders, policymakers, investors, and citizens who follow developments through platforms such as USA Update's business coverage, the question is not only what this means for foreign policy, but how it reshapes the economy, regulation, technology, employment, and the daily lives of ordinary people in the United States and beyond.
The Power of Naming: From Defense Back to War
Names in government are not cosmetic; they are strategic instruments that influence budgets, bureaucratic culture, and public expectations. When the Department of Defense was created in 1949, replacing the earlier Department of War, the new label was designed to convey restraint and legitimacy in the nuclear age. It implied that U.S. military power was fundamentally reactive-protecting the homeland, allies, and the liberal international order-rather than offensive.
By reverting to "Department of War," Washington has revived a term that carries historical weight and contemporary risk. The old Department of War, established in 1789, presided over the early expansion of the United States, the Civil War, and the Spanish-American War. Re-associating today's global military footprint with that legacy inevitably shapes how the U.S. is perceived in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Americas. For allies in the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), whose publics are already wary of foreign interventions, the new name raises uncomfortable questions about whether they are aligning with a defensive partner or a state that defines itself through conflict.
Domestically, the rebrand forces a confrontation with reality. For decades, the U.S. has engaged in wars that were often undeclared but very real-Vietnam, Iraq, Afghanistan, and an array of counterterrorism and drone campaigns from the Sahel to South Asia. The "defense" label offered a moral and political shield, suggesting that these operations were necessary responses to threats. A "war" department, by contrast, invites a more candid debate about when and why force is used, and whether the American public truly supports a posture of enduring global engagement.
For readers tracking political and regulatory developments through USA Update's regulation section, the change also raises questions about how legal authorities for surveillance, domestic deployment, and emergency powers might evolve when framed explicitly under a war mandate rather than a defensive one.
China's "Peaceful Rise" Narrative and the Optics of Power
The timing of the rebrand, juxtaposed with China's recent parade in Beijing, has sharpened a global contrast. Beijing's event was not merely a demonstration of hardware; it was a carefully curated story about national rejuvenation, technological prowess, and stability. Chinese leaders emphasized cooperation, connectivity, and development, aligning the spectacle with long-running initiatives such as the Belt and Road Initiative, which has funded ports, railways, and digital infrastructure across Asia, Africa, Europe, and Latin America. Analysts at institutions like the World Bank and Asian Development Bank have spent years examining how such infrastructure projects reshape trade routes and influence patterns of regional integration.
While China presents its ascent as a civilizational project anchored in economic growth and soft power, the United States has now chosen a vocabulary that highlights kinetic force. For governments in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America, many of which are focused on growth, debt relief, and climate resilience, the optics matter. When leaders compare Beijing's narrative of peaceful development with Washington's Department of War, they must consider not only military guarantees but also domestic political costs and public opinion.
In Europe, where governments must justify defense spending to electorates already burdened by energy transitions and social welfare commitments, the U.S. rebrand complicates the argument for close alignment. For Asia-Pacific partners such as Japan, South Korea, Australia, and Singapore, which rely on U.S. security guarantees while maintaining deep economic ties with China, the new terminology intensifies the balancing act. Readers interested in the broader reconfiguration of alliances can find context in USA Update's international coverage, which tracks how governments from Berlin to Brasília respond to these shifts.
Domestic Militarization: National Guard, Immigration, and Civil Society
The rebranding of the Pentagon comes at a time when Americans are increasingly confronted with images of their own military operating on domestic soil. Over the past several years, the National Guard has been deployed in responses ranging from natural disasters and pandemics to protests and immigration enforcement. The sight of uniformed troops at border zones, in city streets during periods of unrest, or supporting large-scale deportation operations has unsettled communities that historically associated such scenes with faraway conflicts rather than local neighborhoods.
The new Department of War label intensifies concerns among civil liberties organizations and legal scholars who monitor the boundaries between civilian governance and military authority. The Posse Comitatus Act and other legal frameworks were designed to limit the role of the armed forces in domestic law enforcement, yet the practical line between support and enforcement has blurred. As immigration has become a flashpoint in domestic politics, with rising deportations and high-profile enforcement actions, the use of military resources-even in supporting roles-risks normalizing a war-like approach to complex social and economic issues.
For businesses that depend heavily on immigrant labor, including agriculture, construction, hospitality, and logistics, this militarization of immigration policy introduces operational uncertainty and reputational risk. Investors and executives following USA Update's employment and jobs coverage are increasingly aware that labor supply, regulatory enforcement, and political sentiment are intertwined with the broader security narrative.
Venezuela and the Return of Hemispheric Tension
Nowhere has the new U.S. posture been more visible than in the Western Hemisphere. The deployment of U.S. military assets around Venezuela, including naval patrols and air surveillance, has revived memories of earlier eras of interventionism in Latin America. Officially, Washington frames these moves as part of a broader campaign against drug cartels, organized crime, and authoritarian threats. The strike on a suspected cartel vessel in international waters underscored a willingness to conduct kinetic operations under the banner of transnational security.
Regional governments, however, interpret these events through the lens of history. Latin America has a long memory of interventions, coups, and covert operations in which U.S. military and intelligence services played decisive roles. Today, with China and Russia expanding their presence through trade, energy, and arms sales, Washington's more openly militarized posture risks driving some governments to diversify their partnerships further. Organizations such as the Organization of American States (OAS) and regional blocs like MERCOSUR must navigate between security cooperation with the U.S. and domestic constituencies wary of appearing subordinate to a self-declared Department of War.
For Venezuela itself, whose citizens have endured economic collapse, political repression, and mass emigration, the presence of foreign warships and aircraft adds another layer of uncertainty. Humanitarian organizations, including the UN Refugee Agency, warn that any escalation could trigger new refugee flows into Colombia, Brazil, and Caribbean states already struggling with limited resources. Readers can follow how such regional crises intersect with global diplomacy and business through USA Update's news coverage.
The Arithmetic of War: Budgets, Debt, and Opportunity Costs
From a business and finance perspective, the most immediate implication of the Department of War is fiscal. U.S. defense spending has climbed above 850 billion dollars annually, and by 2026, projections by bodies such as the Congressional Budget Office and independent think tanks indicate continued upward pressure driven by modernization programs, operations, and personnel costs. When long-term care for veterans, interest on war-related borrowing, and reconstruction or stabilization efforts are included, the total cost of post-9/11 conflicts alone has been estimated in the trillions of dollars.
Every dollar devoted to war spending has an opportunity cost. Economists at institutions like the Brookings Institution and Peterson Institute for International Economics have repeatedly demonstrated that investments in infrastructure, education, and healthcare generally produce more broad-based employment and productivity growth than equivalent investments in weapons systems. For the United States, which must compete with the European Union, China, and other advanced economies in fields such as clean energy, digital infrastructure, biotechnology, and advanced manufacturing, an overconcentration of capital in military programs can erode long-term competitiveness.
For readers of USA Update's finance section, the link between war spending and macroeconomic stability is increasingly clear. High military outlays contribute to federal deficits and debt, which in turn influence interest rates, currency strength, and investor confidence. In a world where central banks from the Federal Reserve to the European Central Bank must manage inflation, climate risk, and financial innovation, the fiscal drag of perpetual war becomes a strategic liability.
Department of War: 2025 Rebrand Analysis
Interactive exploration of implications and impacts
🏛️ The Historic Shift
What Changed:Pentagon's Department of Defense → Department of War (2025-2026)
Last Used:Original Department of War established 1789, renamed to Defense in 1949
Significance:Marks shift from defensive posture to explicit embrace of conflict readiness
🌍 Global Context
Timing:Occurred amid intensifying US-China competition and geopolitical tensions
China's Response:Beijing staged elaborate military parade emphasizing "peaceful development"
Narrative Contrast:US adopts language of war while China projects cooperation and stability
⚖️ Strategic Implications
Names in government are strategic instruments influencing budgets, bureaucratic culture, and public expectations
The rebrand forces confrontation with reality of decades of undeclared wars and global military engagement
🪖 Domestic Militarization
National Guard increasingly deployed for immigration enforcement, protests, and border operations
Blurring lines between civilian governance and military authority raises civil liberties concerns
🌎 Latin America Focus
US military assets deployed around Venezuela, including naval patrols and air surveillance
Strike on suspected cartel vessel demonstrates willingness for kinetic operations
Regional governments wary given history of US interventions and coups
🤝 Alliance Pressures
NATO Allies:European publics question whether aligning with defensive partner or conflict-oriented state
Asia-Pacific:Japan, South Korea, Australia face intensified balancing act between US security ties and China economic links
🔬 Technology & Innovation
Incentives tilt toward combat applications: AI targeting, drone swarms, hypersonic missiles, offensive cyber tools
Silicon Valley faces ethical debates about defense contracts and corporate responsibility
🌱 Environmental Impact
US military among world's largest institutional fossil fuel consumers
Carbon footprint rivals industrialized nations, complicating Paris Agreement commitments
Strategic Posture: United States vs China
🇺🇸 United States
Branding:Department of War
Message:Conflict readiness, kinetic force
Focus:Military hardware, combat operations
Perception:Offensive posture, permanent war footing
🇨🇳 China
Branding:"Peaceful Development"
Message:Cooperation, connectivity, stability
Focus:Belt & Road infrastructure, economic growth
Perception:Civilizational project, soft power
Global South Perspective
Many governments in Africa, Southeast Asia, and Latin America focused on growth, debt relief, and climate resilience
Comparison of US "war" vocabulary vs China's "development" narrative influences partnership decisions
Infrastructure projects and economic ties increasingly shape diplomatic alignments
1789 - Original Department of War
Established to oversee early US expansion, presided over Civil War and Spanish-American War
1949 - Renamed to Defense
New label designed to convey restraint and legitimacy in nuclear age, implying reactive rather than offensive posture
Post-9/11 Era
Decades of undeclared wars: Vietnam, Iraq, Afghanistan, counterterrorism campaigns across continents
Early 2025 - Rebrand Announced
Government confirms controversial decision to rename Pentagon to Department of War
2025 - China's Military Parade
Beijing stages choreographed display projecting "peaceful development" narrative to global audience
2026 - Full Implementation
New name in use across official documents, congressional hearings, and international diplomacy
💰 Financial Burden
Annual Defense Spending:$850+ billion (2026)
Post-9/11 Total:Trillions when including veteran care, interest on borrowing, reconstruction
Defense spending as percentage of discretionary budget
⚠️ Opportunity Costs
Every dollar for war spending carries opportunity cost for alternative investments
Higher ROI sectors:Infrastructure, education, healthcare generate more jobs and productivity per dollar
Overconcentration in military erodes long-term competitiveness in clean energy, biotech, digital infrastructure
👷 Employment Trade-offs
Defense sector supports hundreds of thousands of jobs in aerospace, shipbuilding, technology
However: equivalent investment in education, healthcare, green infrastructure creates more jobs per dollar spent
Younger workers increasingly prefer careers in sustainability, digital services, creative industries over weapons production
🌍 Economic Fragmentation
Military tensions disrupt shipping lanes, increase insurance costs, create commodity market volatility
Sanctions encourage alternative financial systems, reducing US dollar centrality
BRICS countries expanding trade in local currencies as response to weaponized finance
🌡️ Environmental Toll
Military operations generate tens of millions of tons of CO₂ annually
Jet fuel, diesel, base energy consumption comparable to industrialized nations
Bombings, burn pits, unexploded ordnance leave lasting ecosystem damage
Environmental Costs: War and the Climate Crisis
The environmental consequences of war are often overshadowed by immediate human and political impacts, yet they are central to any long-term assessment of national power. The U.S. military is one of the world's largest institutional consumers of fossil fuels, with a carbon footprint that rivals or exceeds that of many industrialized nations. Jet fuel for aircraft, diesel for ground vehicles, and energy for bases and logistics networks generate emissions that complicate U.S. commitments under the Paris Agreement and broader global climate goals.
Research published by institutions such as Brown University's Costs of War Project and reports from the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute have highlighted how military operations in Iraq, Afghanistan, and other theaters contributed tens of millions of tons of COâ annually, in addition to localized environmental damage. Bombings, toxic burn pits, unexploded ordnance, and damaged infrastructure leave long-lasting scars on ecosystems, water sources, and agricultural land.
As the world accelerates its transition toward renewable energy and climate resilience, the environmental footprint of the Department of War becomes a strategic issue, not merely a moral or scientific one. Countries that lead in green technologies and sustainable infrastructure will shape the future of global growth. If the United States continues to devote disproportionate resources to carbon-intensive military operations, it risks ceding technological and moral leadership to competitors. Readers can explore how energy, security, and climate policy intersect at USA Update's energy coverage.
Technology, Innovation, and the Militarization of the Future
The Pentagon has historically been a powerful engine of innovation. The internet, GPS, advanced materials, and many foundational technologies in today's digital economy originated in programs funded by the U.S. defense establishment. Under a Department of War framework, however, the incentives and narratives surrounding innovation may tilt even more heavily toward combat applications, with implications for both industry and society.
Artificial intelligence, autonomous systems, cyber capabilities, quantum computing, and space technologies are now at the heart of strategic competition. Organizations such as DARPA and major defense contractors are accelerating research into AI-enabled targeting, drone swarms, hypersonic missiles, and offensive cyber tools. While many of these technologies have dual-use potential, their development under a war-centric mandate raises ethical and governance questions. Institutions like the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace and Council on Foreign Relations have warned that the rapid militarization of AI and cyber capabilities could outpace the creation of norms and safeguards.
For the private sector, particularly in Silicon Valley, Austin, Seattle, and other tech hubs, the Department of War brand intensifies debates about corporate responsibility. Major firms such as Microsoft, Google, and Amazon already provide cloud computing, machine learning, and data analytics services to defense and intelligence agencies. Employee activism and public scrutiny have forced some companies to reconsider the types of contracts they accept. At the same time, startups in fields such as cybersecurity, robotics, and space technology see lucrative opportunities in defense procurement.
The challenge for U.S. innovation policy is to harness the benefits of defense-driven research without allowing warfighting imperatives to overshadow civilian applications and ethical frameworks. Readers interested in the evolution of this relationship can follow developments in USA Update's technology section.
War, Work, and the American Labor Market
The military-industrial complex remains a significant source of employment in the United States. From shipyards in Virginia and Mississippi to aerospace plants in California, Texas, and Washington, companies such as Lockheed Martin, Raytheon, Boeing, and Northrop Grumman support hundreds of thousands of direct jobs and many more throughout their supply chains. In regions where alternative industries are weak or underdeveloped, defense contracts can be politically and economically indispensable.
However, when national economic strategy leans too heavily on war-related employment, it can distort labor markets and slow diversification. Studies by groups such as the Economic Policy Institute and International Labour Organization indicate that equivalent investments in education, healthcare, and green infrastructure tend to generate more jobs per dollar spent than defense programs, while also providing broader social benefits.
Younger workers entering the labor market in 2026 are acutely aware of these trade-offs. Many are attracted to careers in sustainability, digital services, and creative industries rather than in weapons production or logistics for overseas deployments. Veterans returning from conflict zones often face challenges in translating their skills into civilian roles, highlighting the need for robust retraining and support programs. For detailed coverage of how war spending intersects with hiring trends, wages, and regional development, readers can turn to USA Update's jobs and employment coverage.
Trade, Sanctions, and the Fragility of Global Commerce
The Department of War's posture has direct implications for global trade and financial systems. Military tensions in key regions-whether the Caribbean, the South China Sea, the Persian Gulf, or the Black Sea-can disrupt shipping lanes, increase insurance costs, and create volatility in energy and commodity markets. Companies planning cross-border investments or managing complex supply chains must now factor in the heightened risk of sanctions, export controls, and sudden regulatory shifts tied to security crises.
Sanctions have become a central instrument of U.S. statecraft, used against states such as Russia, Iran, Venezuela, and North Korea. While sanctions can be powerful, they also impose collateral damage on allies, businesses, and ordinary citizens. Overuse or unilateral application can encourage targeted states and their partners to build alternative financial and payment systems, reducing the centrality of the U.S. dollar and institutions like SWIFT. The efforts by BRICS countries and others to expand trade in local currencies and explore new clearing mechanisms are, in part, responses to the perceived weaponization of the global financial system.
For U.S. firms and investors, this fragmentation introduces new layers of risk. It also raises strategic questions for policymakers: how to balance the use of economic tools for security objectives with the need to preserve an open, predictable global trading system that underpins American prosperity. Readers can explore these dynamics in USA Update's economy coverage, which tracks how war-related policies reverberate through markets and consumer behavior.
Culture, Media, and the Normalization of War
Modern conflict is not only waged on battlefields and in cyberspace but also in the realm of culture and perception. Military parades, live-streamed precision strikes, and sophisticated information campaigns shape how citizens understand and emotionally respond to war. The Chinese parade in Beijing was a masterclass in using spectacle to project an image of orderly, disciplined strength. In the United States and allied countries, entertainment industries-from film and television to video games-often frame war as a stage for heroism, strategy, and high technology.
This cultural environment matters because it can desensitize societies to the realities of conflict. When war is depicted as clean, surgical, and dominated by advanced weaponry, the long-term human costs-displacement, trauma, economic collapse-fade into the background. At the same time, critical media, independent journalism, and documentary filmmaking continue to expose the darker side of militarization, creating a contested narrative space.
Platforms like USA Update's entertainment coverage play a role in examining how war is represented in popular culture and how those representations influence public opinion, recruitment, and political support for military spending. For a democracy, maintaining a space where citizens can access diverse perspectives on war is essential to ensuring informed consent for policies that carry profound human and economic consequences.
Humanitarian and Moral Dimensions
Beyond strategy and economics lies the core humanitarian question: what is the human cost of structuring national identity and policy around war? Conflicts in Iraq, Afghanistan, Syria, Yemen, and other regions have produced massive displacement, with millions of refugees and internally displaced persons whose lives have been upended. Organizations such as the International Committee of the Red Cross and Doctors Without Borders continue to document the long-term health, psychological, and social impacts of protracted warfare.
For many communities in the Middle East, North Africa, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa, U.S. military operations-whether direct or through partners-are part of a broader tapestry of violence that includes local militias, extremist groups, and rival state interventions. The rebranding of the Pentagon as the Department of War reinforces perceptions in some of these regions that the United States is more comfortable with kinetic solutions than with sustained diplomatic or development engagement.
At home, veterans and their families live with the aftershocks of war long after media attention has moved on. Issues such as post-traumatic stress disorder, long-term disability, and difficulties reintegrating into civilian life are persistent challenges for the Department of Veterans Affairs and local communities. The moral legitimacy of U.S. global leadership depends, in part, on how seriously the country takes its responsibility to those it sends into harm's way. Readers can find reflections on how war shapes community life, family dynamics, and social cohesion in USA Update's lifestyle coverage.
Democracy, Trust, and the Risk of Overreach
A core tension in the Department of War rebrand lies in the relationship between militarization and democratic governance. The United States presents itself as a champion of democratic values worldwide, yet the expansion of military and intelligence powers, especially in the wake of 9/11, has raised persistent concerns about surveillance, transparency, and checks and balances. Laws crafted to address external threats-such as the Patriot Act and various emergency authorities-have sometimes been applied in ways that affect domestic dissent and civil liberties.
As war becomes a more explicit organizing concept for U.S. security policy, the risk is that exceptional measures become normalized. Internal deployment of the National Guard, the use of advanced surveillance tools within the homeland, and the blending of military and law enforcement roles can erode public trust if not carefully constrained and transparently overseen. For a democracy, legitimacy depends on the consent and confidence of its citizens. If large segments of the population perceive that war priorities consistently outweigh investments in health, education, and economic opportunity, political polarization and disillusionment can deepen.
Readers following regulatory developments and civil liberties debates through USA Update's regulation section will recognize that the Department of War rebrand is not only about foreign policy; it is also a domestic governance issue that will shape the balance between security and freedom for years to come.
Alternative Paths: Diplomacy, Cooperation, and Shared Prosperity
Despite the gravity of the shift to a Department of War, the future is not predetermined. History offers examples of strategic choices that favored diplomacy and reconstruction over extended military occupation. The Marshall Plan after World War II, which focused on rebuilding European economies, created durable alliances and markets that benefited both the United States and its partners. Arms control agreements during the Cold War, such as the Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) and subsequent treaties, reduced the risk of nuclear catastrophe while maintaining stable deterrence.
In the 21st century, global challenges such as climate change, pandemics, cybercrime, and financial instability cannot be resolved through military means alone. Institutions like the United Nations, World Health Organization, and International Monetary Fund remain critical arenas for cooperation, even as they face criticism and calls for reform. By investing more heavily in diplomacy, development assistance, and multilateral problem-solving, the United States could leverage its economic and cultural strengths to advance a model of leadership less centered on war.
Economic cooperation, too, is a powerful peace-building tool. Countries deeply integrated through trade and investment are statistically less likely to engage in open conflict. By supporting fair trade, resilient supply chains, and inclusive growth, the U.S. can help reduce the underlying grievances that fuel instability. For businesses and policymakers interested in how trade, investment, and regulation intersect with security, USA Update's business coverage provides ongoing analysis.
Citizens, Public Opinion, and the Road Ahead
Ultimately, the trajectory of the Department of War will be shaped not only by presidents, generals, and legislators, but also by citizens and civil society. In the United States, public opinion has become more skeptical of large-scale interventions after the long, costly campaigns in Iraq and Afghanistan. Younger generations, in particular, prioritize climate action, economic equality, and social justice, and are less inclined to view military power as the primary measure of national greatness.
Grassroots movements, veteran advocacy groups, academic institutions, and independent media all contribute to a more nuanced conversation about war and peace. Platforms like USA Update serve as important spaces where business leaders, policymakers, and engaged citizens can access informed analysis across domains-economy, technology, energy, lifestyle, and more-and evaluate how military decisions intersect with their own interests and values.
As of 2026, the United States stands at a genuine crossroads. The rebranding of the Pentagon as the Department of War has crystallized debates that have simmered for decades about the role of force in American identity and strategy. Whether this moment becomes a pivot toward greater militarization or a catalyst for rebalancing toward diplomacy and sustainable prosperity will depend on choices made in Washington, in boardrooms, and in communities across the country.
For now, the world is watching closely, allies are recalibrating, competitors are adjusting their narratives, and ordinary people-from the United States to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America-continue to hope that their futures will be defined less by war and more by stability, opportunity, and peace.